Debugging ARENA Web Browser Visually
When running programs in Python or Unity, you have a plethora of debug tools at your disposal to debug lines of code. For debugging the visual elements of rendered scenes, here are some other tools to help, and some guidance of where they are useful. Each tool has an expansive or limited capacity to display object messages (Read Objects), and add/change/delete object messages (Write Objects), as noted
| Visual Object Editors | Format | Read Objects | Write Objects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Python Console Interface | MQTT | All | None |
| Build JSON | JSON | All | All |
| Build 3D | 3D | All | All |
| A-Frame Inspector | 3D | All | None |
| Unity Editor | 3D | Most1 | All |
| WebXR API Emulators | 3D | Camera/Hands | Camera/Hands |
| AR Builder | 3D | All | Primitives/GLTFs |
1 The arena-unity library is still in development. Objects currently rendered are all Primitives, GLTFs, Lights, Lines, Text, Images. Others still to be rendered are: PCD, Threejs, URDF, UI Panels, Gaussian Splat.
Python Console Interface
There is a console interface tutorial to the arena-py Python library. This is designed to have a way to inspect the program from the console, without having to send a heartbeat or write your own command/response interface.
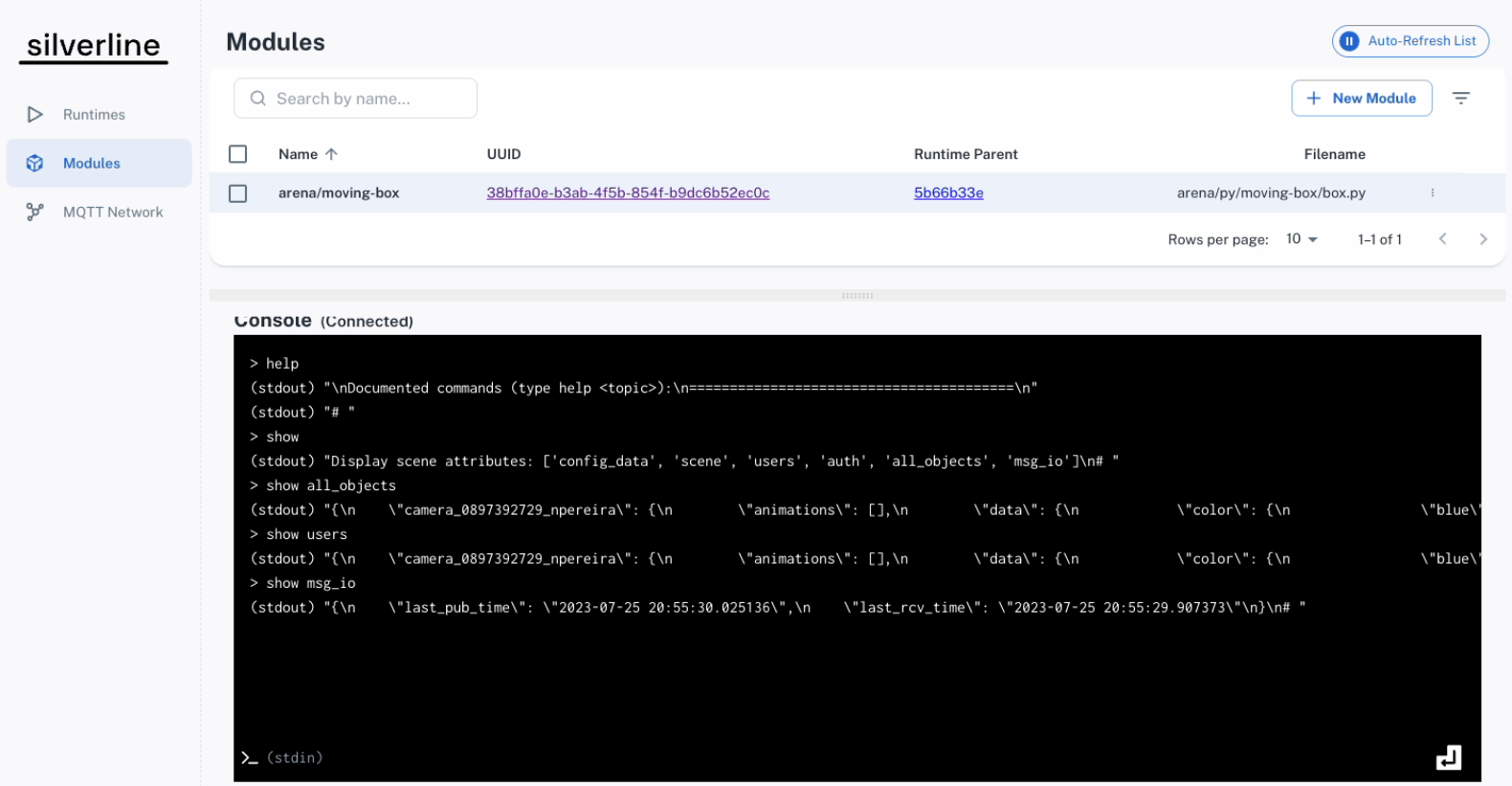
Build (JSON) Page
There is a JSON scene build tutorial for ARENA scenes. This is for editing persisted scene objects and configuration in JSON format with full support of all objects and their components.
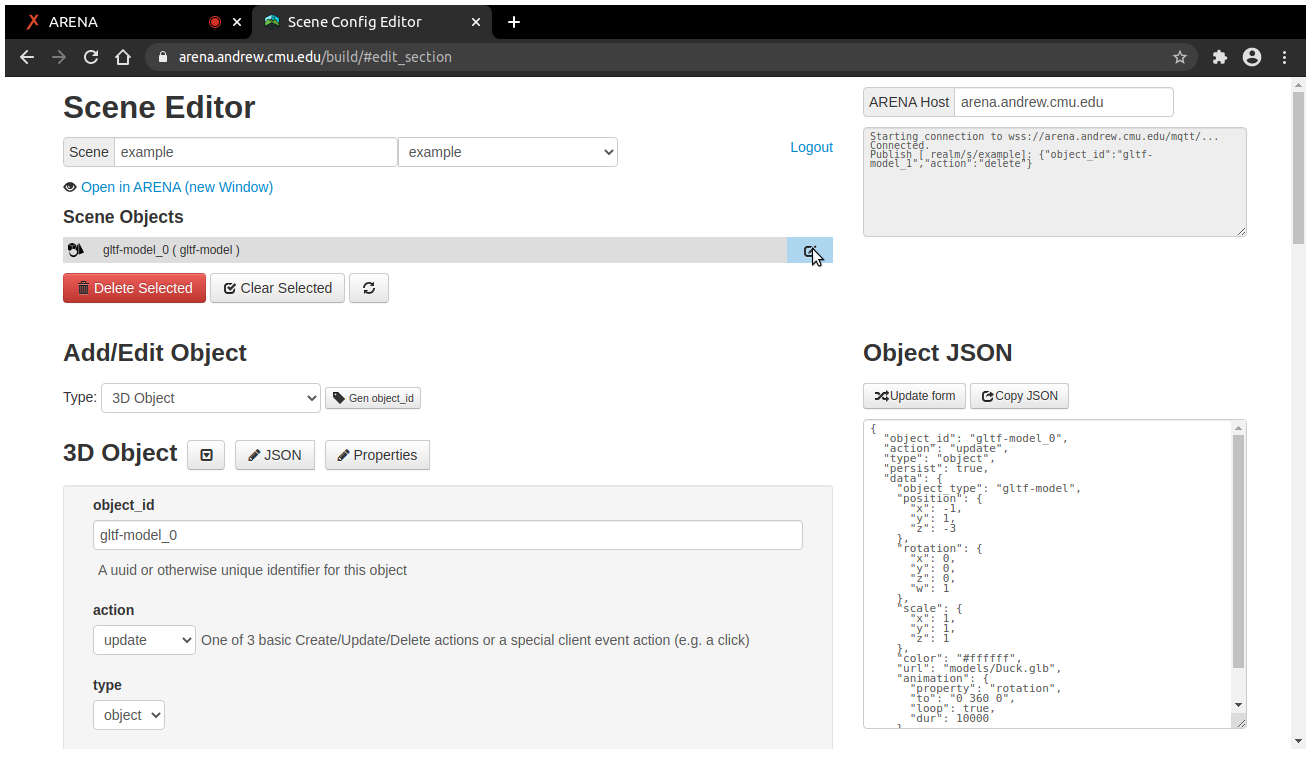
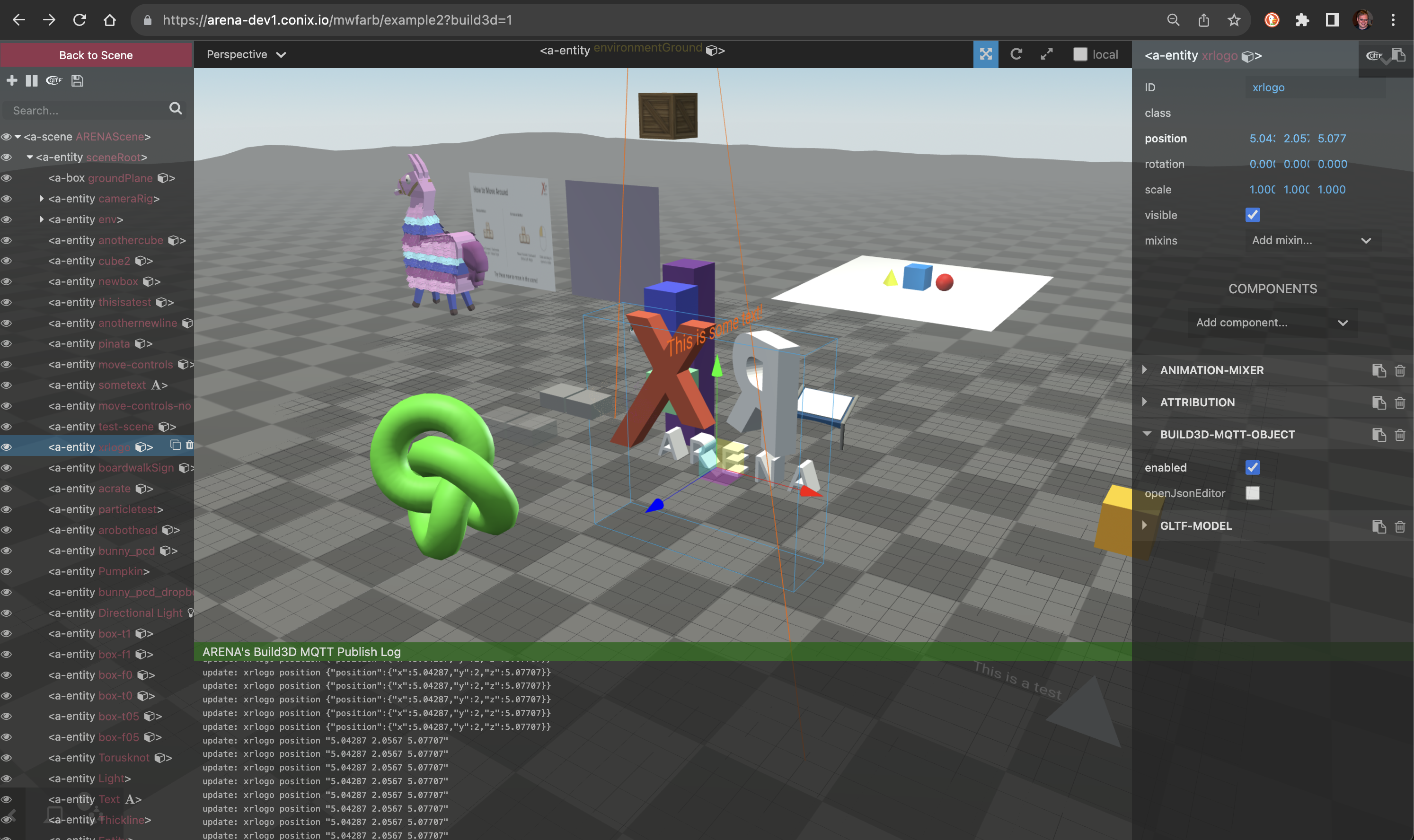
Build 3D
There is a Build 3D tutorial for ARENA scenes using Build 3D. This is for editing persisted scene objects and configuration in 3D just as they would be on the 3D browser view. Build 3D leverages the A-Frame Inspector, with some critical differences, namely that changes are shared to other users.
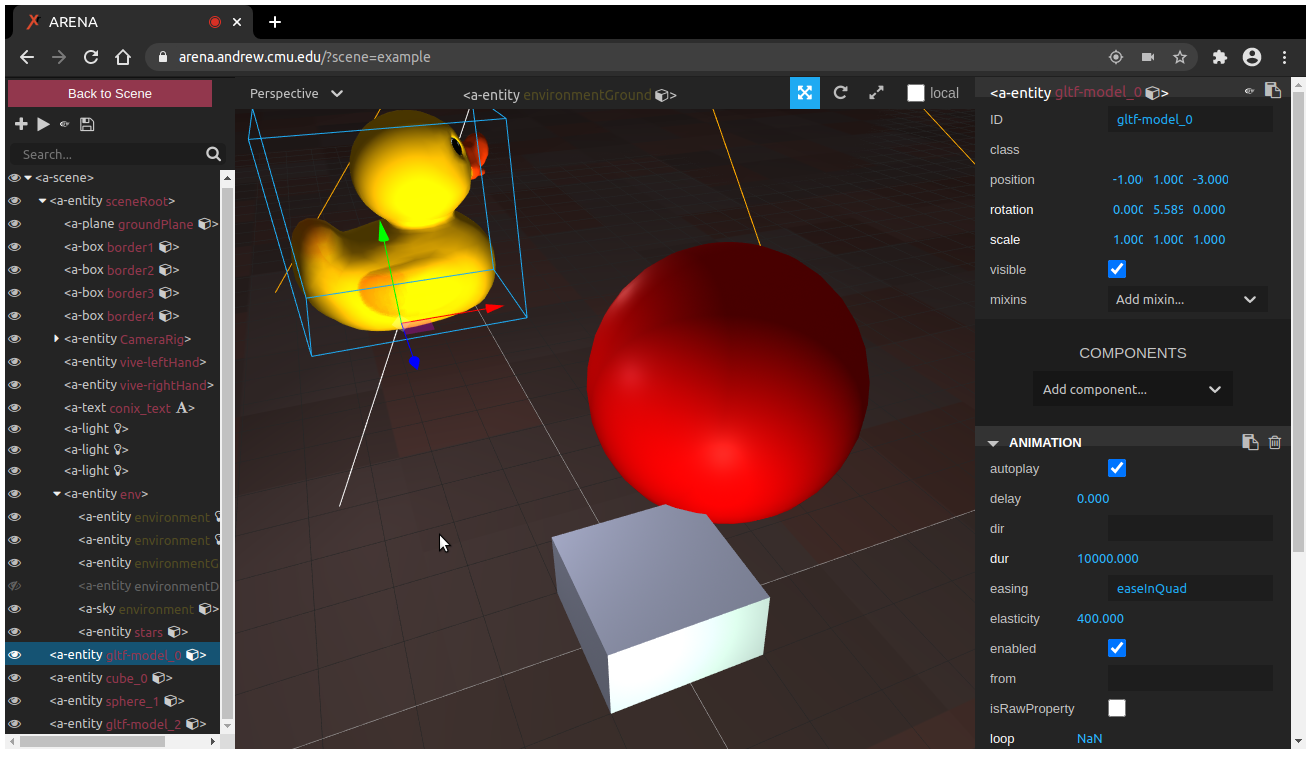
A-Frame Inspector
There is a A-Frame Inspector tutorial for ARENA scenes using A-Frame Inspector. NOTE: The default A-Frame Inspector does not publish MQTT updates. Any changes you make are local only.
warning
A-Frame Inspector and Build 3D are similar, but operate critically differently. Learn to tell them apart: The A-Frame Inspector has opaque black control panels, and Build 3D has transparent black control panels.
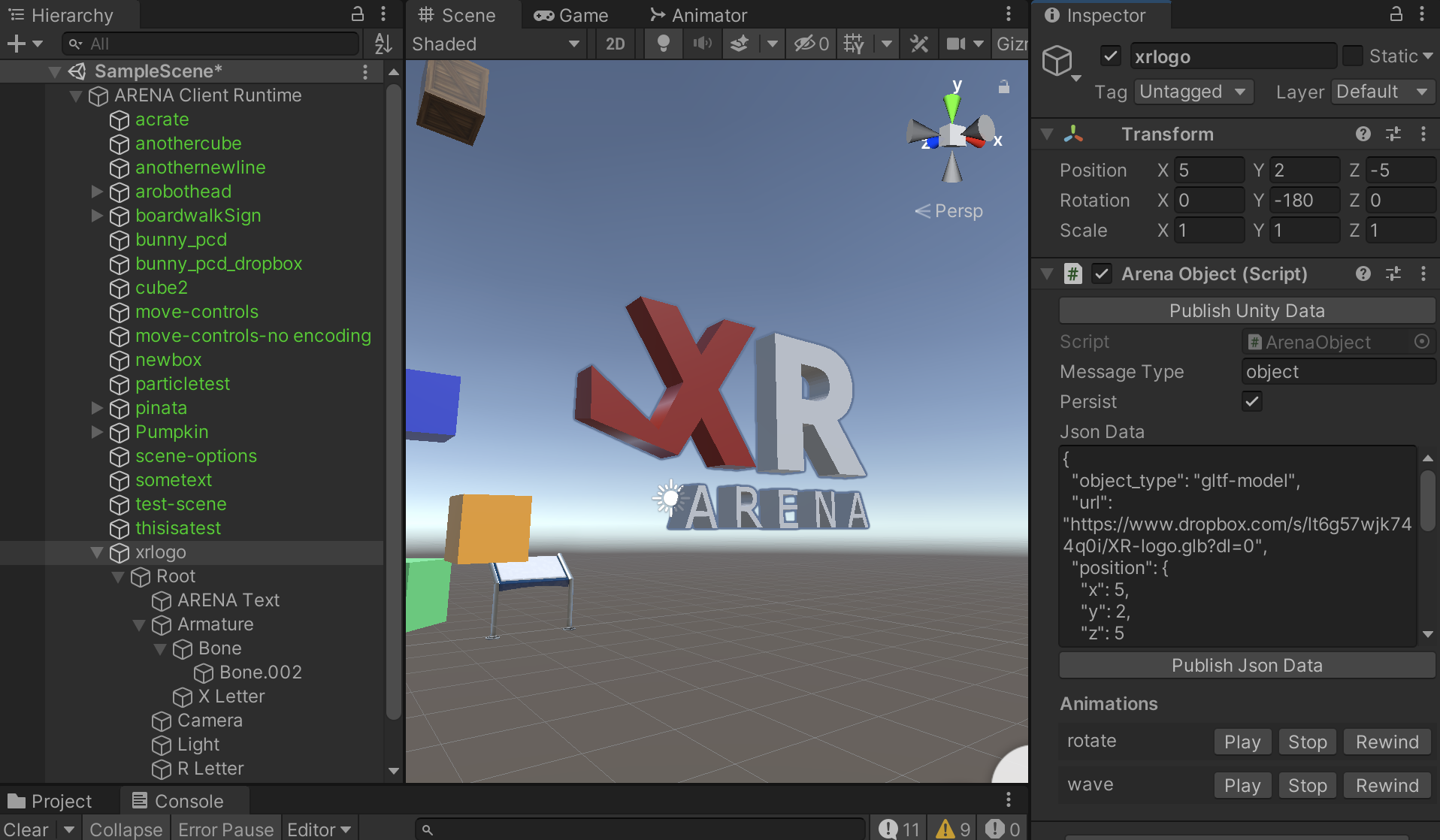
Unity Editor
There is a Unity 3D scene editing tutorial for ARENA scenes. This is for editing persisted scene objects and configuration in 3D in a Unity rendering window.
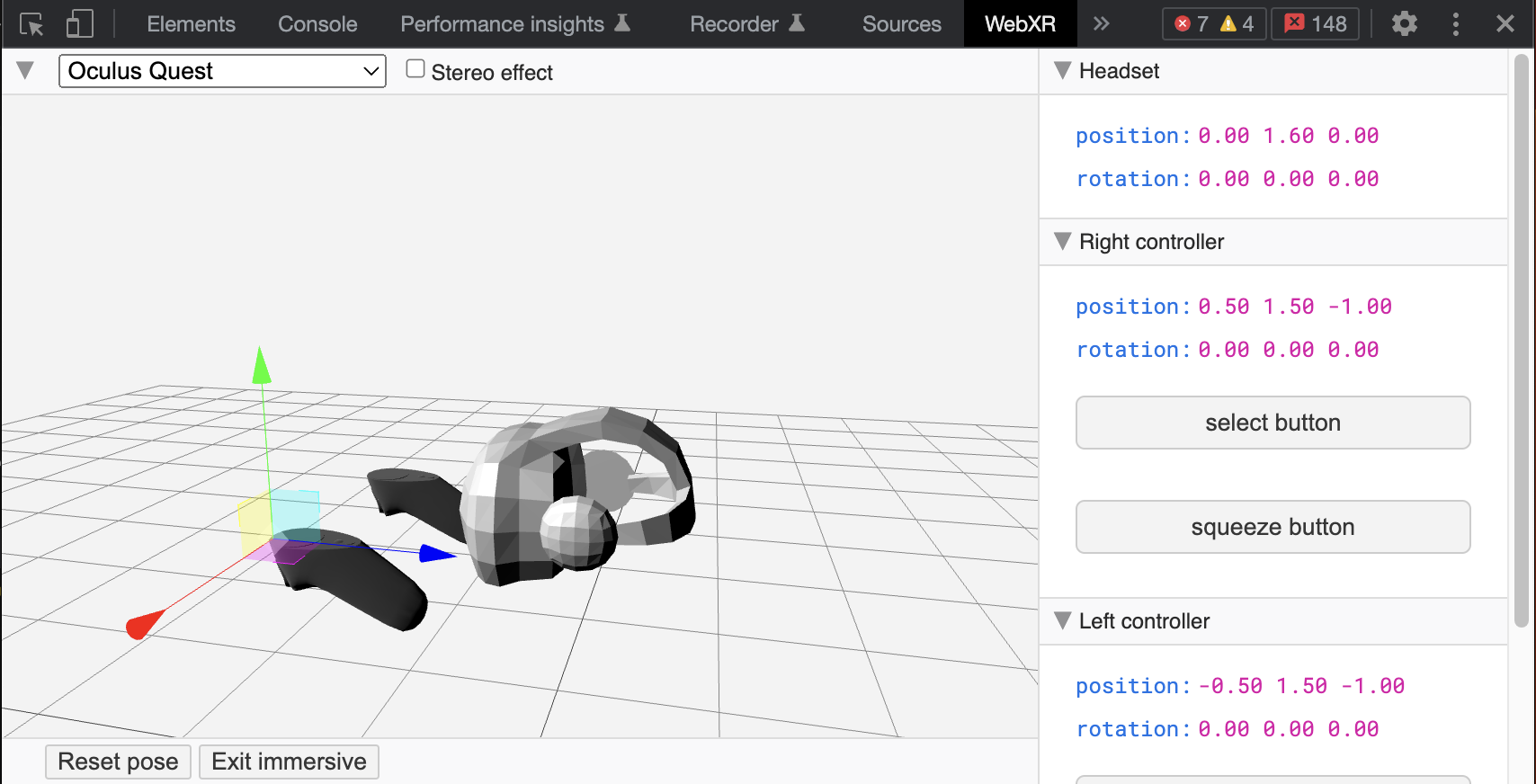
WebXR API Emulators
Since ARENA’s web view runs on WebXR, we can use one of the WebXR API Emulators to test Immersive VR (headset) features without a headset.
- WebXR API Emulator by Mozilla Mixed Reality for Firefox and Chrome. Emulates Quest, Go, Gear VR, Vive, Cardboard devices.
- Immersive Web Emulator by Meta for Chrome. Emulates Quest, Rift devices.
Usage:
- Go to the one of the above browser addon stores to install.
- Open your ARENA scene web view and the ARENA detects that you have a XR device (emulated) and it will let you enter the immersive (VR、AR) mode.
- Open the
WebXRtab in the browser developer tool (Firefox, Chrome) to control the emulated devices. You can move the headset and controllers, and trigger the controller buttons.
AR Builder
We also have a Python program, AR Builder (ARB), which you can use to create and edit objects for your scene. You can use it in VR (virtual reality) as a way to edit your scene and save changes to the persistence database. Importantly, you can use it in AR (augmented reality) in combination with supported browsers and localization techniques to anchor scene objects in physical space. See our section on miXed Reality (XR) for details.
note
Check out the Platforms Section for details on browsers and platforms that support XR in ARENA.
In either case, ARB allows any user in the scene to edit, so it can be used collaboratively by multiple users remotely as VR, in person as AR, or as XR (miXed Reality), a combination of both.
goal
Use a tool like A-Frame Inspector to navigate a real-time ARENA scene graph and seek out an object to discover its properties and feel free to change them and observe the rendered changes.